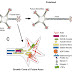
Hedgehog family of proteins is signaling proteins which control the cell growth, survival, fate and pattern (almost every aspect) of the vertebrate body plan. The name was derived from the short and spiked phenotype of the cuticle of the Hh mutant Drosophila larvae.
Except in C.elegans, It is found in both vertebrates and invertebrates. In C.elegans, it has several proteins homologous to the Hh receptor Ptc.
There are three subgroups in hedgehog protein family:
A. Desert hedgehog (Dhh)
B. Sonic hedgehog (Shh)
C. Indian hedgehog (Ihh)
Both the vertebrates and invertebrates, hedgehog binds to the receptor patched (Ptc) and activates a signaling cascade which ultimately drives the activation of the zinc finger transcription factor (Ci in Drosophila and GLI-3 in mammals) leading to activation of specific target genes.
A. Desert hedgehog protein:
The expression of this protein is restricted to gonads only which includes sertoli cells of testis and granulose cells of ovaries. Its deficiency in mice has not shown any significant phenotypic changes, but in males it leads to infertile since there is absence of mature sperm. Dhh is required for organogenesis, Leydig cell formation and sex cord formation. In the absence of Dhh signaling, the size of the precursor Leydig cell population is unaffected but these cells have reduced expression of the transcription factor steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1). This is the likely cause of impaired expression of steroidogenic enzymes and ultimately testosterone, which is required for virilisation and spermatogenesis.
B. Sonic hedgehog protein:
Basically it’s a mammalian hedgehog signaling molecule which is expressed during the early vertebrate embryogenesis in midline tissues such as node, notochord and floor plate to control the patterning of the left –right and dorso ventral axes of the embryo. In the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) of the limb bud, Shh is expressed and critically involved in patterning of the distal elements of the limbs. During organogenesis also, it is expressed in and affects the development of most epithelial tissues. In the absence of the Shh protein will lead to cyclopia, and defects in ventral neural tube, somite and foregut patterning. The protein is very important for hypothalamic and pituitary development.
C. Indian hedgehog protein:
The expression of this protein is limited to number of tissues which includes primitive endoderm and prehypertrophic chondrocytes in the growth plates of bones. During embryogenesis its absence in the embryo has lead to its death due to poor development of yolk sac vasculature.
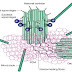
Hedgehog signaling pathway:
A general outline of the hedgehog signaling pathway in the cell is shown. After the translation of hedgehog, it undergoes multiple processing steps that are required for generation and release of the active ligand from the producing cell.
Maturation of the protein (Hedgehog)
1. The signaling molecule undergoes a self cleavage soon after the signal sequence is removed. The cleavage is catalyzed by its own C terminal domain that occurs between the conserved glycine and Cysteine residues.
2. The peptide between the two residues is rearranged to form a thioester. Now, oxygen of the –OH group of cholesterol attacks the -CHO of the thioester. This lead to displacing of the sulfur and cleaving of the Hh protein into two parts:
Ø A C -terminal processing domain with no known signaling activity.
Ø An N- terminal Hh signaling domain (HhN) of approx 19 kDa that contains an ester linked cholesterol at its C terminus. This cholesterol modification will result in association of the HhN with the plasma membrane of the cell.
3. A palmitic acid moiety which is required for the HhN activity is added to the N terminus of Hh by the acyl transferase skinny hedgehog, this process is called palmitylation.
Without the cholesterol modification, the protein can escape through the dispatched protein easily and can be palmitoylated later during the transport or at the receiving cell. Hence Cholesterol modification role is found to negligible or more study need to be done on it. But palmitylation role is found to be important for generating soluble multimeric Hh protein complexes and also for long range signaling in vertebrate.
Signaling process:
Finally the matured Hh protein binds to the membrane protein called Dispatched, which will let the protein to be secreted out of the cell. Loss of the dispatched protein will cause the accumulation of the Hh protein in the producing cells and failure of long range signaling occurs.
The concentration and transport of the Hh protein is controlled by the extracellular proteins such as you/Scube 2 (in the case of zebra fish) as well as proteins on the surface of cells situated between those producing and receiving hedgehog signals (for example, patched (PTC1) hedgehog interacting protein (HIP), exostosin (EXT1), CDO (interference hedgehog (IHOG) in Drosophila) and its relative BOC).
In the absence of the Hh protein, the patched receptor (Ptc) inhibits the Smo (GPCR smoothened) receptor present either on the cell surface or on a vesicle inside the cell. This inhibition will lead to the activation of GLI3R protein which indirectly inhibits the class I Transcription factors such as PAX6, PAX7. Therefore Hh target genes are not transcribed.
But when the Hh protein is released by the secreting cells, it binds to the Ptc1 receptors leading to activation of the Smo receptor. This inturn will inhibit the GLI3R formation and supports the formation of GLI2/3A from GLI2/3 with the help of protein like wimple, flexo, KIF3A and Rab23.
Finally GLI2/3A will activate the transcription factor (class I and II) and also GLI1 leading to transcription of Hh targeted genes.