Bax, Par-6 and aPKC is not required for axon and dendrite specification
Overexpression of Baz or Par-6, aPKC does not have any effect on axon morphology or number in Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly). New study shown by Melissa M Rolls from penn state and Chris Q Doe from univ of oregon.
GSK3b- The master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
GSK-3 deletion have resulted in suppression of both intermediate neural progenitors and postmitotic neurons generation and massive hyperproliferation of neural progenitors along the entire neuraxis.
EphrinBs reverse signalling and control dendrite morphologies
EphrinB signalling pathway regulates the dendrite morphology and number of spines.
No need of Protein synthesis in distal axon for growth cone response to the cues
New study have shown that protein synthesis is not required for growth cone response to guidance cues. The study was investigated over chick neuron by researchers from univ of Minneapolis, Minneapolis.
SOX 2 gene decides the neural stem cells fate
New study shown that SOX2 maintains the potential for neural crest stem cells to become neurons in the PNS. The research was led by Dr.Alexey Terskikh at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham)
Oct 30, 2011
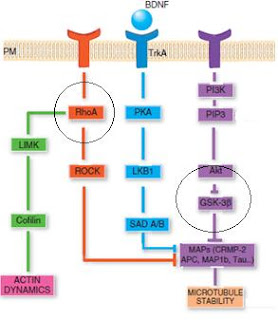
Negative regulators of Neuronal polarity
Oct 13, 2011
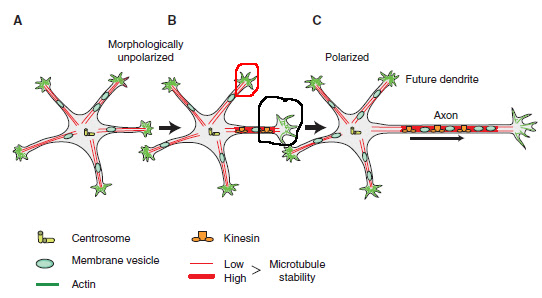
Neuronal Polarity Introduction
Cytoskeleton Role in Neuronal polarity
- The Microtubules rapidly convert the molecular signals into structural changes modulating cell shape.
- They possess an intrinsic polarity.
Oct 12, 2011
Actin and Microtubules regulators
- WAVE (wiskott Aldrich syndrome protein [WASP] family verprolin homologous protein)
- Ena/VASP (Vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein)
- Profilin
- ADF (actin depolymerization factor)/ cofilin
Neuronal polarity regulation
Oct 11, 2011
PAR protein in axon specification and neuronal polarity
s. no
|
Par proteins
|
In C.elegans
|
Drosophila homolog
|
Mammalian homolog
|
Involvement in neuronal polarity?
|
1
|
Par1
|
Serine/Threonine kinase
|
Par 1
|
MARK kinase
SAD kinase
|
Yes
|
2
|
Par2
|
Zinc finger and ATP binding motif (ubiquitination pathway)
|
Not conserved
|
Not conserved
|
unknown
|
3
|
Par3
|
Scaffold (PDZ domains)
|
Bazooka
|
mPar3 (also called as ASIP PHIP)
|
Yes
|
4
|
Par4
|
Serine/Threonine kinase
|
Par4
|
LKB1
|
Yes
|
5
|
Par5
|
14-3-3 protein
|
Par5
|
14-3-3 protein
|
Unknown
|
6
|
Par6
|
Scaffold
|
Par6
|
mPar6
|
Yes
|
Axon Specification
In establishing a polarized neuron, the initial event is the specification of a single axon where one of the neurite will grow into a axon.